“The tongue is but three inches long, yet it can kill a man six feet high”
Tongue, in a human body is a boneless, muscular organ that helps the health professionals in getting to know much about your overall health. A small, movable organ in mouth, if examined properly can do wonders in determining many of the diseased conditions affecting humans at a very early stage.
The tongue has two parts: the body and the root. Body faces upwards and consists of different papillae or taste buds that help in recognizing different types of tastes in food we eat. The root part helps the tongue in attaching to the floor of the mouth.
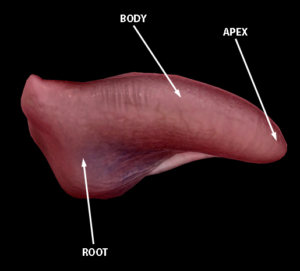
While examining, first inspect the body of the tongue for any type of ulcer, swelling, white or red patch or any other unusual finding present on tongue. Note for the movements of the tongue, locate the painful points on the tongue on both body and the root part. If you can locate any abnormality, it is time to visit your oral physician.
Some of the symptoms that can help the patient in locating if he/she has diseased tongue include pain/soreness at different locations on tongue, burning sensation while having spicy foods, rough patch or any abnormal coatings on tongue, dryness or cracking or fissuring on body surface of tongue, any growth, ulcer, blister or eruptions on the tongue, loss of taste or any pigmentation on the tongue. If you are suffering from any of these, then it is the right time to visit your specialized dentist.
Your oral physician will help you in diagnosing your disease, whether it a localized tongue disease or a manifestation of your general health. Some of the tongue diseases are:
- Inherited, developmental disease: Aglossia, Macroglossia, Microglossia, Bald tongue, Fissured tongue, etc
- Lingual (root surface) mucosa disease: Tertiary syphilis, Ulcers, Traumatic injuries, Pigmentation
- Conditions found in specific regions of tongue: a. Dorsum (body of tongue): Traumatic ulcer, Lichen planus, Fungal infection (oral candidiasis), Tuberculosis, Syphilis, Diabetes Mellitus, Geographic tongue, Vitamin B deficiency, Anaemia, Leukemia, Papilloma, Fibroma, Pyogenic granuoma, Fissured tongue, oral cancer b.Ventral (root part) surface: Ulcer, Ranula, Salivary gland tumor
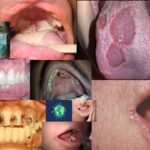
- Syndromes associated with tongue diseases: Glossopalatine ankylosis syndrome, Meckle’s syndrome, Orofacial digital syndrome, Pierre Robin syndrome, etc. Now, let us discuss some tongue diseases-: 1.Aglossia: congenital (by birth) absence of tongue. It is rarely found

AGLOSSIA 2.Macroglossia: tongue is disproportionately larger in size. The pressure of the teeth on the enlarged tongue lead to indentation marks on the sides of tongue. Some of the causes of macroglossia include congenital cause, down syndrome, cretinism, acromegaly, amyloidosis, hypothyroidism, tongue infection, syphilis, pneumonia, pemphigus, rheumatic fever, tuberculosis, actinomycosis, diabetes, uremia, sarcoidosis etc.

MACROGLOSSIA 3.Ankyloglossia: it is tongue tie that restricts the movement of tongue

ANKYLOGLOSSIA 4.Cleft tongue: a complete cleft or bifid tongue presents as deep groove in the midline of dorsal surface. It is seen presented with certain syndromes like Meckle’s syndrome, etc

BIFID TONGUE 5.Foliate papillitis: one of the papillae on body surface of the tongue, i.e., foliate papillae becomes inflamed and enlarged and presents with pain and burning sensation in that region of the tongue.

FOLIATE PAPILLITIS 6.Oral hairy leukoplakia: Mostly observed in patients infected with HIV. It involves lateral border or the sides of the tongue and is presented with white to grayish hair like projected growths.

ORAL HAIRY LEUKOPLAKIA
Tongue plays a very important role in diagnosing and treating many of the diseases of human body at an early stage. Hence, never ignore what your tongue is trying to project you.