Viruses are submicroscopic structures containing RNA (ribonucleic acid) or DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). They can reproduce only within the specific living cell. Viruses may be classified according to the nucleic acid present in them. For example, coronavirus, orthomyxovirus, paramyxovirus, rhabdovirus, picornavirus, retrovirus are some of the RNA viruses. DNA viruses include herpes virus, poxvirus, adenovirus, papovirus etc.
Among all the viruses, the most common viral infection among the human beings is caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV). Primary infection is caused when a healthy person comes in contact with the infected secretions from eyes, mouth or skin of an affected person. At the time of primary infection, usually the person remains asymptomatic. In case, the symptoms arise, the most common being fever, certain oral signs like blisters in the mouth. After, a primary infection, the herpetic virus remains latent in the neural cells of the person and will be reactivated only when triggered by some specific stimuli such as cold or any other physical or emotional stress.
The Herpes Simplex Virus has two variants broadly, i.e., HSV I and HSV II. The infection from HSV I commonly affect the region above the waist while HSV II infection causes lesions below the waist especially in the genitals. If there is an incidence of oral sex, then oral lesions can be found after HSV II infection.
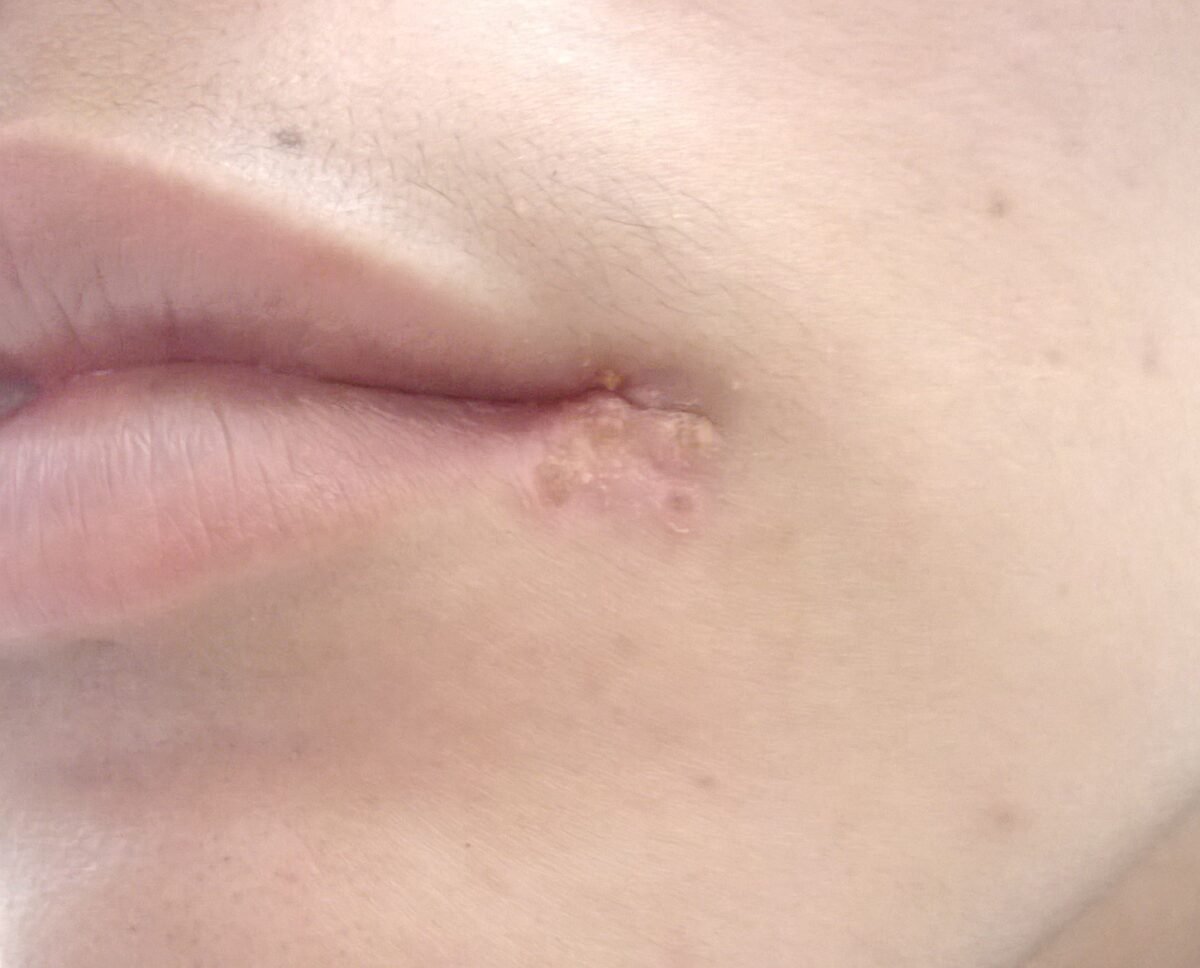
The primary infection of Herpes Simplex Virus is known by different names like ‘fever blister’, ‘cold sore’, ‘herpes labialis’ etc. As it is the primary infection, hence no history of prior infection will be present. After this primary infection, the virus will move in the nerve ganglion like trigeminal nerve ganglion in case of HSV I and lumbosacral nerve ganglion by HSV II and remains latent there. The virus can remain latent in these ganglions even for years and will be reactivated only when triggered by certain stimuli.
The infection occurs at the time of close personal contact between a healthy and an affected person. The vertical infection from mother to her newborn child can also be caused by the vaginal secretions of the affected mother at the time of delivery. Also, it has been seen that people belonging to lower socioeconomic status have earlier exposure to the disease.
In most of the cases, children and young adults going to schools and colleges are affected with the virus. The virus has an incubation period (period between the infection and the first symptom) of 5-7 days with prodormal symptoms (symptoms that arise before the occurrence of any visible lesion) of fever, headache, nausea, vomiting and malaise. Within a few days of such symptoms, the mouth becomes extremely painful. Pain is aggravated while eating food and even swallowing of food becomes difficult. Regional lymphadenopathy or localised swelling and pain in the lymph nodes is a common presentation. Following this, small vesicles with thin wall appear all over the mouth especially on the hard palate, attached gingiva (gums) and tongue. Sometimes, such lesion may also be found on the skin. The area surrounding the vesicle will be inflamed. These vesicles will first grow slowly then will rupture leaving small, oval shaped ulcers with size varying from 2-6 mm. With the progression of the disease, the ruptured ulcers will coalesce and form larger ulcers with grayish white or yellowish base. The margins of these big coalesced ulcers are uneven, well demarcated and inflamed. In cases, where lesions occur on the lips, the lesions may become so painful that it can hinder the chewing and speech of the affected person. Pharynx (part of throat) becomes inflamed making the swallowing difficult.
The biopsy of the lesion helps in proper approach towards the diagnosis of the disease. Multinucleated giant cells and ballooning degeneration are seen in the cytological examination. Lipschutz bodies are the characteristic finding.
No treatment is required as the disease is self-limiting and complete healing will take place in about 7-10 with no scar left.
The recurrent or secondary herpetic infection may occur in the presence of any precipitating factor like surgery of the trigeminal ganglion, low serum IgA, trauma to lips, dental extraction, upper respiratory tract infection. In some cases, it has been seen that fever, sunburns, fatigue, menstruation, pregnancy may precipitate the infection.
The recurrent infection of the herpes may have varying intervals, from nearly every month in some patients. The prodormal symptoms include burning and tingling sensation. The recurrent herpes labialis occur as gray or white vesicles on lips. Size of the lesion may vary from 1-3 mm in diameter to even larger lesions. The healing will itself occur in 7-10 days.
Though the herpetic lesion is self-limiting and healing takes place on its own within7-10 days, still assistance by a doctor/dentist will help in minimizing the pain of the patient.